Table of Contents
ToggleHolistic 7 major nutrients for our food –
Water,Corbohydrete ,fat Proteins ,Vitamins Minerals And Fibers .-
Overall nutrients supported wellbeing healthy life.All these holistic nutrients play an important role in the structure, development and maintenance of the body. To stey healthy,it is necessary to consume each nutrition in the RDA amount daily.But often we do not consume adequate amounts of the essential in our diat or our food is cooket through refined processes.
Most people consume greins and cooked food in abundance but do not consume enough alkaline raw vegetables,fruitsand other natural foods . Due to incomplete absorptionby the body , we ar not ableto get the nutrients availeble in our food .
As a result , lack of nutrition or unbalanced diet leads to premature old age, aging skin ,weakness, pain in the body , hair fall, lack of vision, loss of appetite , lack of sleep , fatigue ,sugar, oestoporosis, breakout of nails, weakness ofmuscles,increasing body fat and loss of appetite.
Along with this,it is equaly importand when ,wtat and how much we should not eat. we have to apply this holistic nutrients .
Water is a holistic nutrients our life:
- Water is essential for life and is a fundamental component of a healthy, balanced diet. Here are Water is crucial for maintaining proper hydration levels in the body. It helps regulate body temperature, transport nutrients, and facilitate various physiological processes.
Cell Function:
- Water is a major component of cells, playing a vital role in cell structure and function. It is involved in the processes that keep cells healthy and functioning properly.
Digestion:
- Water is necessary for the digestion and absorption of nutrients. It helps in breaking down food, transporting nutrients across the digestive system, and facilitating the elimination of waste.
Joint Lubrication:
- Water helps lubricate joints and cushions organs and tissues. It contributes to the overall functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
Detoxification:
carbohydrates:
Carbohydrates are one of the three main macronutrients, alongside proteins and fats. They are a primary source of energy for the body. Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. There are three main types of carbohydrates:
- Simple Carbohydrates:
- Also known as sugars, these include glucose, fructose, and sucrose. They are found in fruits, vegetables, and refined sugars.
- Complex Carbohydrates:
- These are found in foods like whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. Complex carbohydrates consist of multiple sugar molecules and provide a more sustained release of energy.
- Fiber:
- Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that is not fully digested by the body. It is found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Fiber is essential for digestive health and can contribute to feelings of fullness.
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing energy for various bodily functions, including brain function and physical activity. It’s important to choose sources of carbohydrates wisely, focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods rather than highly processed and sugary items. The recommended amount of carbohydrates can vary based on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and overall health.
Water is magic of natuer and is a holistic nutrient for the human body .
Is this conversation helpful so far?

Carbohydrates are one of the three main macronutrients, along with proteins and fats. They are essential for providing energy to the body and are found in a variety of foods.
Carbohydrates can be classified into three main types:
Simple Carbohydrates (Sugars):
- Sources: Found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products, as well as added sugars in sweets and processed foods.
- Examples: Glucose, fructose, sucrose (table sugar).
Complex Carbohydrates (Starches):
- Sources: Found in whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables.
- Examples: Bread, rice, pasta, potatoes.
Dietary Fiber:
- Sources: Found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes.
- Examples: Soluble and insoluble fiber.
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy, especially for the brain and muscles. When you consume carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose, which is then used for energy or stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen for future use.
It’s important to include a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in your diet for overall holistic health. The quality of carbohydrates matters, and it’s generally recommended to focus on whole, unprocessed sources like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes rather than relying on refined or added sugars. The exact amount of carbohydrates needed varies based on factors such as age, activity level, and individual health goals. If you have specific dietary concerns,
it’s advisable to consult with a health consultent professional or a registered dietitian
Fats are essential
fats are essential macronutrients that play crucial roles in the human body. They are important for energy storage, insulation, cushioning organs, and aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Dietary fats come in various forms, including saturated fats, unsaturated fats, and trans fats. It’s essential to consume fats in moderation and choose healthy sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil for optimal health.
If you had a different question in mind, please provide more details so I can assist you better.
and injoining holistic healthy fife
:
Protiens is our block bulilding of body – Proteins are essential macronutrients that play a crucial role in the structure and function of the human body. They are composed of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. holistic Proteins are involved in various physiological processes, including:
- Building and Repair: Proteins are necessary for the growth, maintenance, and repair of tissues in the body. This is particularly important for muscle growth and repair.
- Enzymes: Many enzymes, which act as catalysts for biochemical reactions, are proteins. Enzymes are involved in processes such as digestion and metabolism.
- Hormones: Some hormones, such as insulin and growth hormone, are proteins that regulate various physiological functions.
- Immune System Function: Antibodies, which are proteins, play a crucial role in the immune system, helping to defend the body against infections and diseases.
- Transportation: Proteins can act as carriers, transporting substances such as oxygen in the blood (hemoglobin) or nutrients across cell membranes.
- Structure: Proteins contribute to the structural integrity of cells and tissues. Examples include collagen in connective tissues and keratin in hair and nails
- Holistic nutrients protien RDA par 1 gram = par 1 k.g.
Dietary sources of protein include meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds. It’s important to include an adequate amount of protein in your diet to support overall health and well-being. The recommended daily holistic protein intake can vary based on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and health go
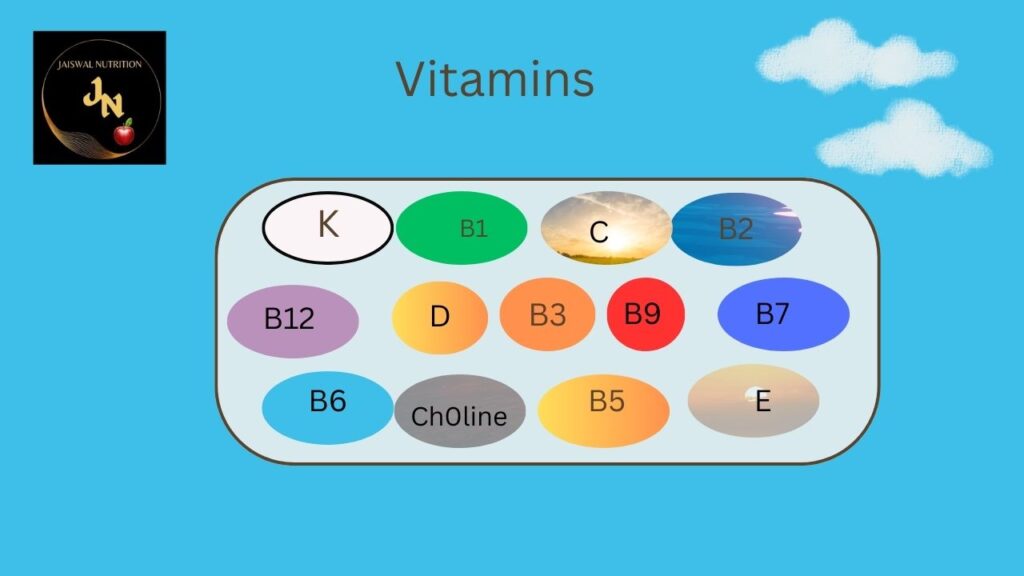
Holistic Vitamins
hrough a balanced and varied diet. In some cases, holistic supplements may be recommended if a person has difficulty getting enough vitamins from their diet or has specific medical conditions.
Deficiencies or excesses of certain vitamins can lead to health issues. For example, vitamin deficiencies can cause conditions Holistic Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential for various physiological functions in the human body. They play crucial roles in growth, development, metabolism, and overall health.
There are two main types of vitamins: water-soluble and fat-soluble.
Water-Soluble Vitamins:
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid): Important for collagen synthesis, immune function, and antioxidant defense. Found in citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli.
- B Vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12): Involved in energy metabolism, red blood cell formation, and neurological functions. Found in various foods, including whole grains, meat, dairy products, and leafy greens.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins:
- Vitamin A (Retinol): Essential for vision, immune function, and skin health. Found in liver, carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens.
- Vitamin D: Critical for bone health and calcium absorption. Produced in the skin in response to sunlight and found in fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks.
- Vitamin E (Tocopherols): An antioxidant that protects cells from damage. Found in nuts, seeds, vegetable oils, and leafy greens.
- Vitamin K: Necessary for blood clotting and bone health. Found in leafy greens, broccoli, and soybeans.
It’s important to obtain vitamins t like scurvy (vitamin C deficiency) or rickets (vitamin D deficiency). On the other hand, excessive intake of fat-soluble vitamins can lead to toxicity. Therefore, it’s crucial to maintain a balanced and nutrient-rich diet. If you have specific dietary concerns or health conditions, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietiti
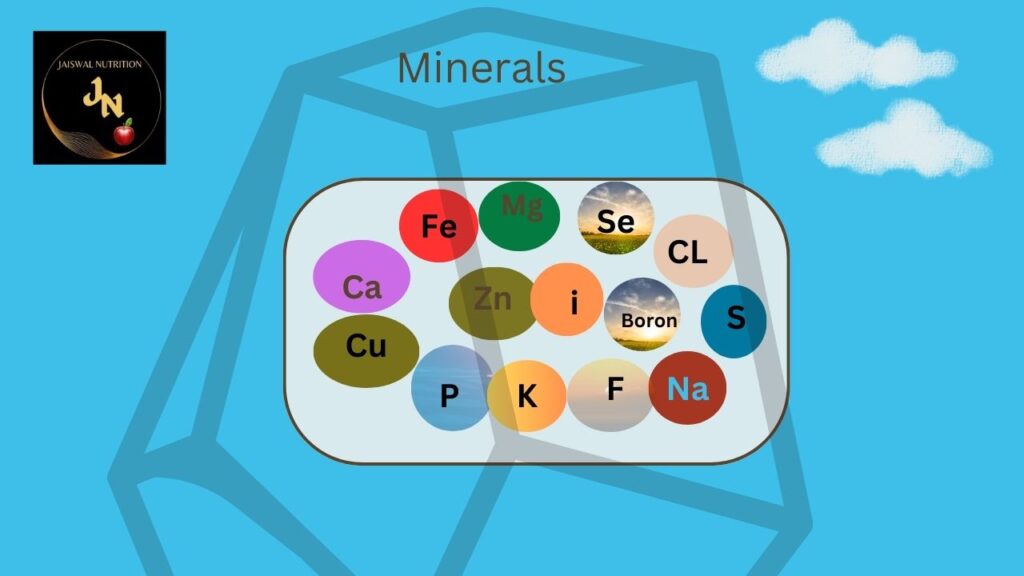
Holestic minerals are less then a treasure for the BODY.
Minerals are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in various physiological functions in the human body. They are classified into two categories: macro-minerals and trace minerals. Both types are necessary for maintaining good health.
Here are some important minerals and their roles:
Macro-minerals:
Calcium:
Essential for bone and teeth formation, blood clotting, and muscle function.
Phosphorus:
Works with calcium in bone formation, and is involved in energy metabolism.
Magnesium:
Important for muscle and nerve function, blood sugar regulation, and bone health.
Sodium:
Regulates fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contractions.
Potassium:
Balances sodium levels, helps with nerve transmission and muscle contractions, and regulates fluid balance.
Chloride:
Maintains fluid balance and is a component of stomach acid.
Trace minerals:
Iron:
Essential for oxygen transport in the blood (hemoglobin) and energy production.
Zinc:
Involved in immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis.
Copper:
Plays a role in iron metabolism, connective tissue formation, and antioxidant defense.
Selenium:
Acts as an antioxidant and is important for thyroid function.
Iodine:
Essential for thyroid hormone synthesis.
Manganese:
Involved in bone formation, blood clotting, and reducing inflammation.
Fluoride:
Important for dental health, strengthening tooth enamel.
Chromium:
Assists in glucose metabolism.
It’s important to obtain these holistic minerals through a balanced and varied diet. While most people can get sufficient minerals through food, in some cases, supplements may be recommended, especially if there are specific deficiencies. It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before starting any supplementation. Consuming a diverse range of holistic nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy or dairy alternatives, can contribute to meeting your mineral needs.

Dietary Fiber
Dietary fiber, often referred to simply as fiber, is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest or absorb. Instead of being broken down and absorbed, fiber passes through the digestive system relatively intact.
There are two main types of dietary fiber: soluble and insoluble.
Soluble Fiber:
- Sources: Found in foods such as oats, barley, beans, lentils, fruits (especially apples and citrus fruits), and vegetables.
Benefits:
- Helps lower blood cholesterol levels.
- Regulates blood sugar levels by slowing the absorption of sugar.
- Aids in weight management by providing a feeling of fullness.
Insoluble Fiber:
- Sources: Found in whole grains, nuts, seeds, vegetables (especially dark leafy greens), and the skins of fruits.
- Benefits:
- Supports digestive health by adding bulk to the stool and preventing constipation.
- May help prevent certain digestive disorders.
Key Benefits of Holistic Dietary Fiber:
Digestive Health:-
Fiber adds bulk to the stool, softens it, and helps prevent constipation. It can also aid in the prevention of diverticulitis and hemorrhoids.
Weight Management:
- High-fiber foods often require more chewing and take longer to eat, promoting a feeling of fullness and potentially reducing overall food intake.
Blood Sugar Control:
- Soluble fiber can help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of sugar, making it beneficial for individuals with diabetes.
Heart Health:
- Soluble fiber can help lower blood cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Colon Health:
- A diet rich in fiber is associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer.
To increase your fiber intake, it’s recommended to include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds in your diet. It’s also important to drink plenty of water along with a high-fiber diet to help prevent constipation. The daily recommended intake of fiber varies by age, sex, and other factors, but in general, adults are advised to consume around 25 to 30 grams of holistic fiber per day.
conclusion
The understanding of the seven essential holistic nutrients in our food is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals, fiber, and water collectively play vital roles in supporting various bodily functions, from providing energy and building tissues to regulating metabolism and enhancing immune function. Achieving a balanced and diverse diet that incorporates these holistic nutrients in appropriate proportions is fundamental for promoting optimal health and preventing nutritional deficiencies. Recognizing the interconnectedness of these nutrients underscores the importance of embracing a holistic approach to nutrition, ensuring that our dietary choices contribute to the harmonious functioning of our body systems and ultimately supporting a robust and resilient state of wellness.
